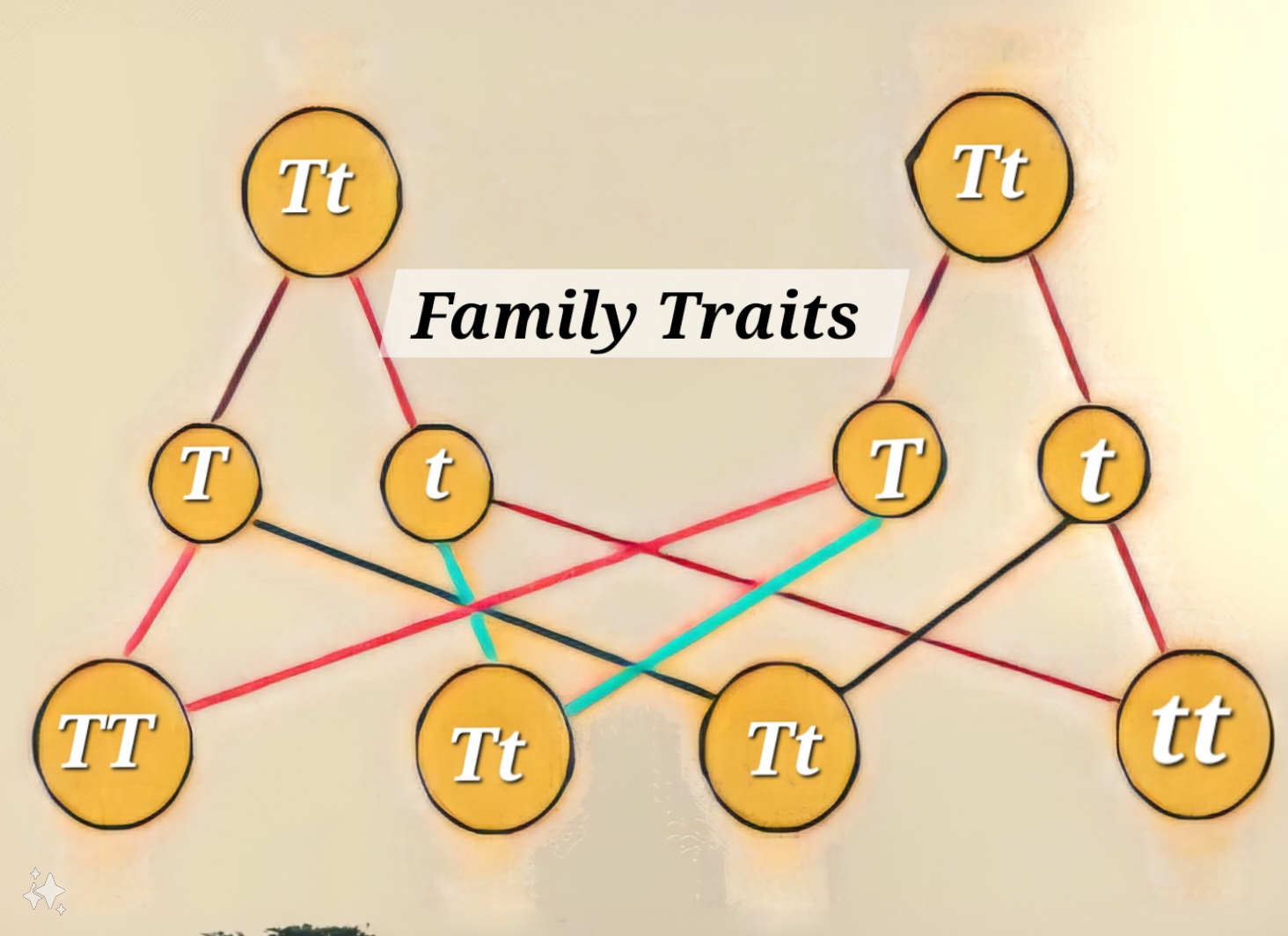
This Basic Science lesson for Junior Secondary School 3 (JSS 3) students introduces the concept of family traits. Students learn to define and differentiate between inherited and acquired traits, providing examples of each. The lesson explains how genes and heredity pass traits from parents to offspring, using visual aids like family trees to illustrate this process. The concepts of dominant and recessive traits are also introduced, highlighting their role in trait expression. Finally, the lesson emphasizes the importance of understanding family traits, particularly concerning health and personal identity.
- Teacher: Josephine Ezema
- Teacher: Michael Ezema








